
Featured Projects
- E-TraMS – Enhancements of Transportation Management Software
- Philippine ElectroChemical Arsenic Remediation
- IWASTO – Integrated Waste Analysis, Survey and Technological Options
- e-SMART – Eco-system Modeling and Material Transport Analysis for the Rehabilitation of Manila Bay
- Data Strengthening for Child Road Traffic Injury Prevention (CRTIP) Programme
- Modelling and Estimation of Transportation Energy Demand of the Philippines
- SWERVE – Enhanced Severe Wind Vulnerability Curves of Key Building Types in the Philippines
- Characterization of Plastic and Microplastic Wastes in Urban Rivers Leading to Laguna Lake
- PAVE – Prototype Automated Visual survey Equipment
- ExPerlite – Determination of Appropriate Expansion of Perlite to Conform to Standards of Lightweight Aggregates for Use in Construction
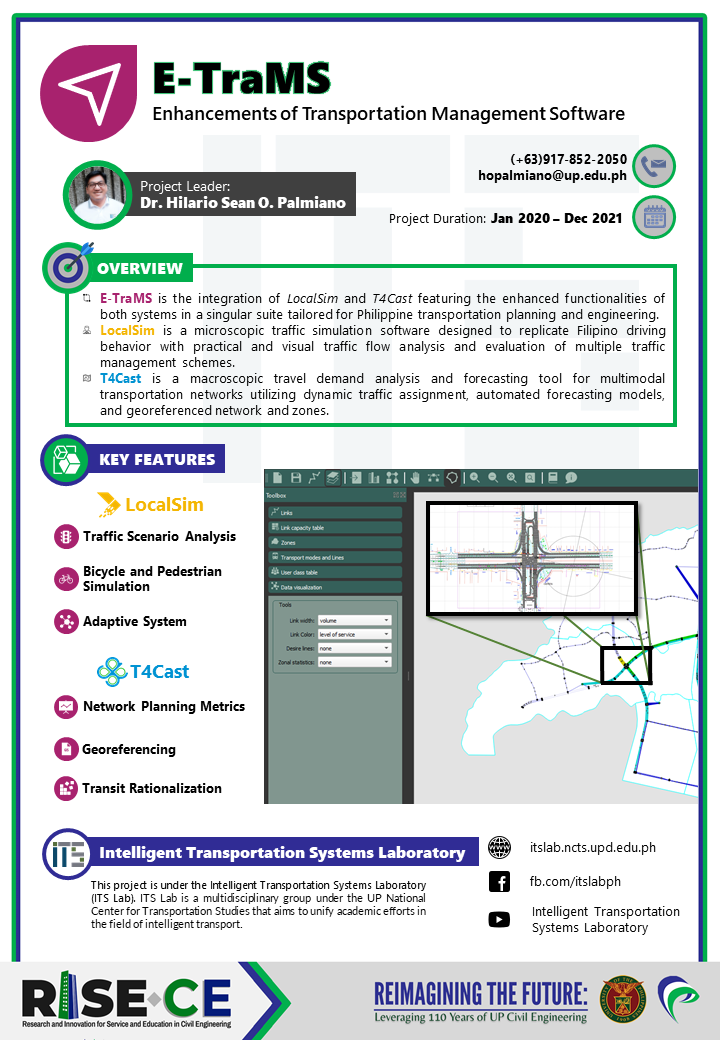
E-TraMS – Enhancements of Transportation Management Software
Responding to the need for effective traffic management in the country, Project E-TraMS aims to package LocalSim and T4Cast into one software suite – a powerful tool that will provide improved usability and functionality for the target users while building the capacity of LGUs to manage small-scale traffic (by using LocalSim’s microscopic traffic simulator) and plan long-term solutions that adapt to the ever-changing traffic demand profile in urban regions (by using T4Cast’s traffic forecasting outputs).
The project is led by Dr. Hilario Sean Palmiano under the ITSlab PH of UP National Center for Transportation Studies and is funded by DOST PCIEERD.
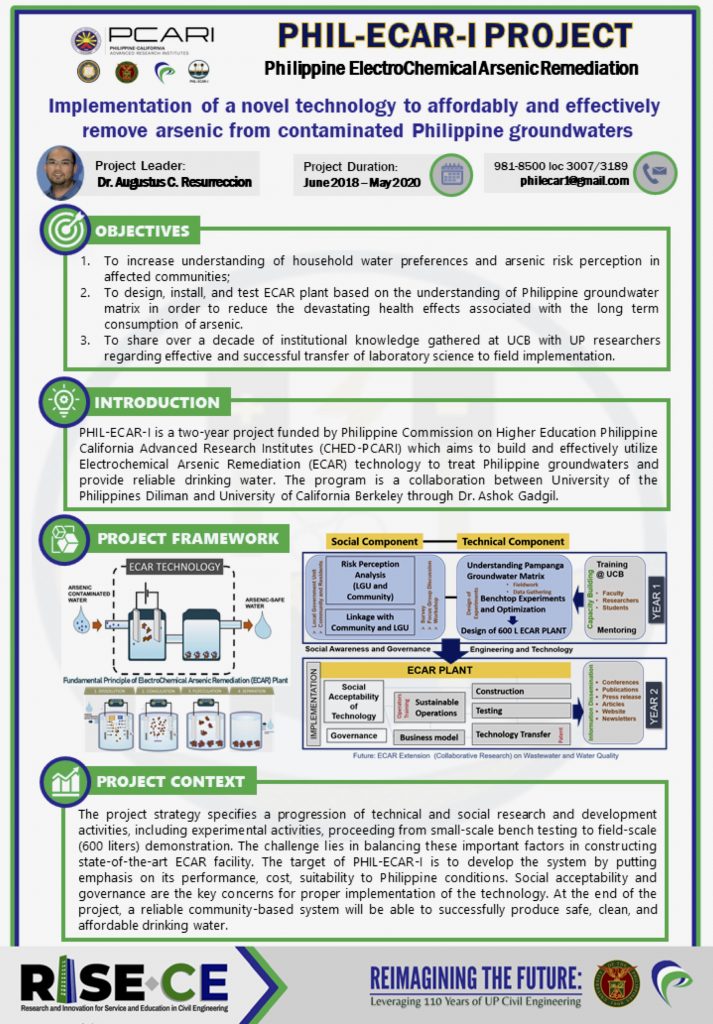
Philippine ElectroChemical Arsenic Remediation
The Philippine ElectroChemical Arsenic Remediation (Phil-ECAR-I) is a two-year project funded by CHED PCARI – Philippine California Advanced Research Institutes which aims to build and effectively remove arsenic from contaminated groundwaters in the Philippines using ECAR Technology. The program is a collaboration between UP Diliman and the University of California Berkeley. The project leader is Dr. Augustus Resurreccion.

IWASTO – Integrated Waste Analysis, Survey and Technological Options
Project IWASTO is a two-year project led by Dr. Maria Antonia Tanchuling, under the IM4ManilaBay Program and funded by DOST PCIEERD. It primarily aims to develop an integrated solid waste information and technology management system for selected cities which form part of the Manila Bay watershed.
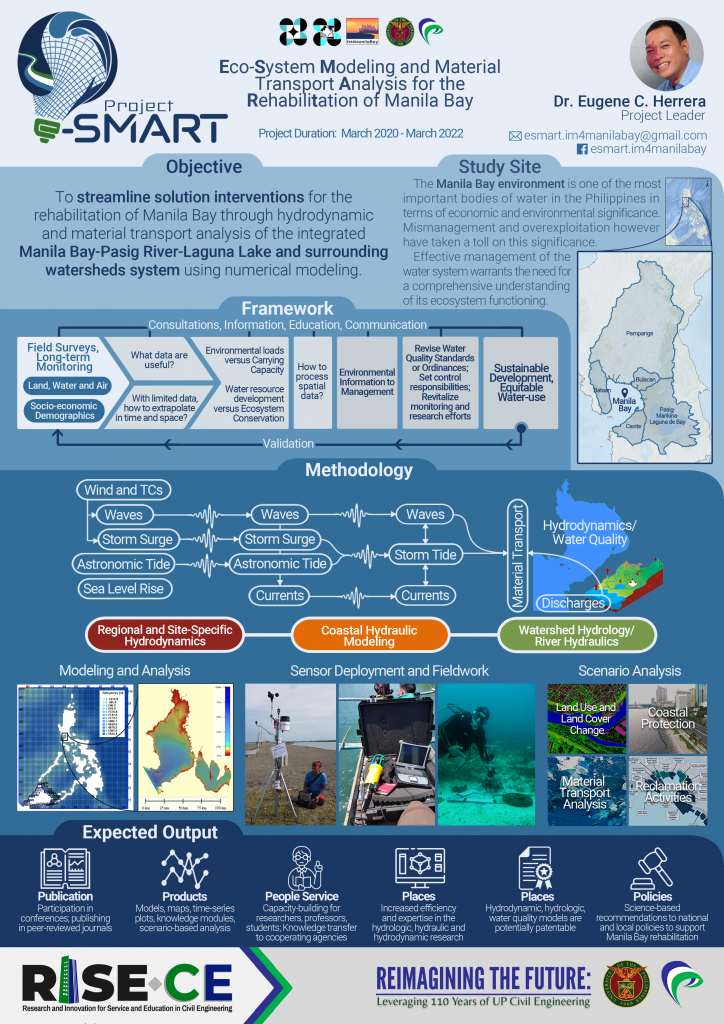
e-SMART – Eco-system Modeling and Material Transport Analysis for the Rehabilitation of Manila Bay
Project e-SMART is a two-year project led by Dr. Eugene Herrera under the IM4ManilaBay Program and funded by DOST PCIEERD. It primarily aims to streamline solution interventions for the rehabilitation of Manila Bay through hydrodynamic and material transport analysis of the integrated Manila Bay-Pasig River-Laguna Lake and surrounding watersheds system using numerical modeling.

Data Strengthening for Child Road Traffic Injury Prevention (CRTIP) Programme
Towards current and more reliable data and assessments for Child Road Traffic Injury Prevention.
The Data Strengthening for Child Road Traffic Injury Prevention (CRTIP) Programme in the Philippines is part of a program that includes improvement of road safety and journey to school for children. This project is led by Dr. Ricardo Sigua and Dr. Jose Regin Regidor, implemented by UP National Center for Transportation Studies in collaboration with Safe Kids Philippines, Human Development and Empowerment Services (HDES), and the cities of Valenzuela and Zamboanga for the pilot study.
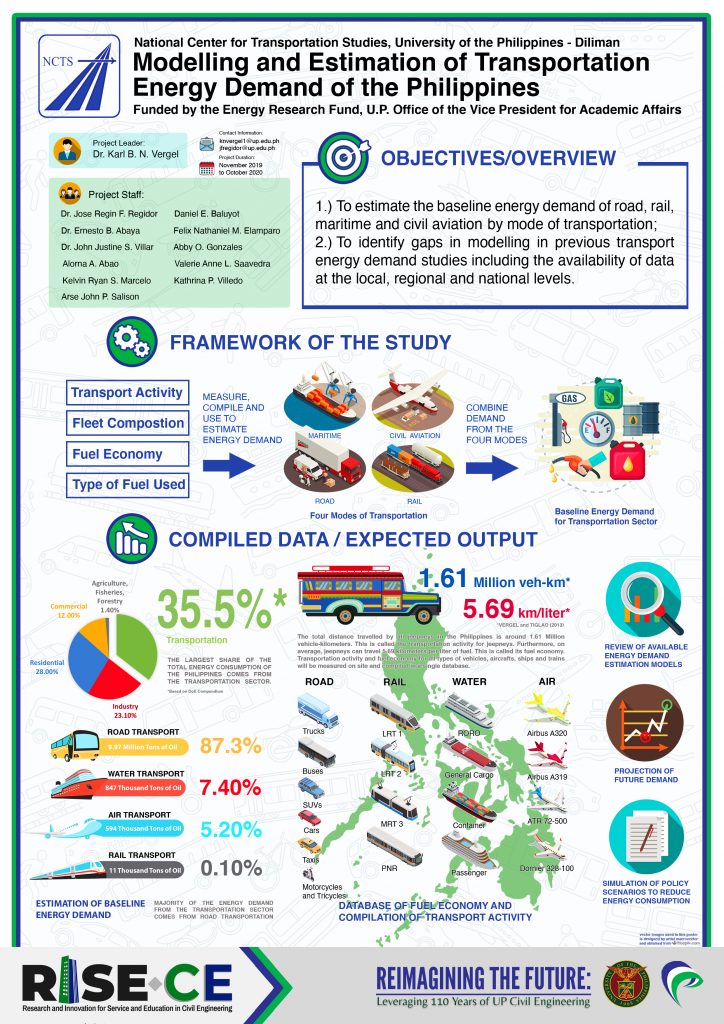
Modelling and Estimation of Transportation Energy Demand of the Philippines
The Modelling and Estimation of Transportation Energy Demand of the Philippines Project is funded by the Energy Research Fund of the UP-OVPAA and it aims to estimate the baseline energy demand for domestic road, rail, maritime, and aviation transportation using a bottom-up approach. It will also attempt to model policies to reduce the growth of transportation energy demand. This is project is led by Dr. Karl B.N. Vergel and is implemented by UP National Center for Transportation Studies.

SWERVE – Enhanced Severe Wind Vulnerability Curves of Key Building Types in the Philippines
Vulnerability models are used to estimate how much damage occurs to a given building type subjected to severe wind speeds. Incorporating the vulnerability curve into building exposure databases of a community overlaid by hazard maps that show the return periods of different wind speed will yield information on regions that will be highly devastated by Typhoons.
Project SWERVE aims to identify key building types in Cebu that are vulnerable to severe wind loading and to develop corresponding vulnerability curves throug computational and empirical methods. This project is funded by DOST PCIEERD and led by Asst. Prof. Timothy John Acosta.
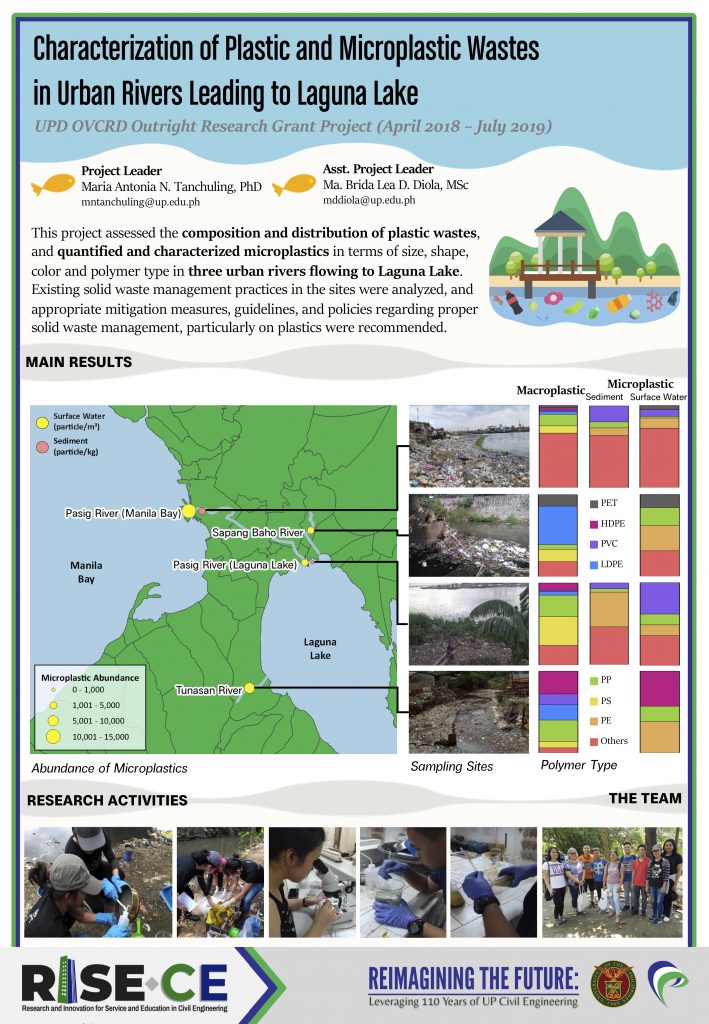
Characterization of Plastic and Microplastic Wastes in Urban Rivers Leading to Laguna Lake
This project is funded by the UPD OVCRD, and is led by Dr. Maria Antonia Tanchuling. It assessed the composition and distribution of plastic wastes, and quantified and characterized microplastics in terms of size, shape, color and polymer type in three urban rivers flowing to Laguna Lake.

PAVE – Prototype Automated Visual survey Equipment
Project PAVE aims to improve the local road monitoring system. It aims to automatically detect the defects on the road including potholes, cracks, vegetation, pavement markings and other defects as specified in Department Order 41 of Department of Public Works and Highways. This equipment aims to assist road quality inspectors for faster data gathering and lessen the risk of their jobs. This faster means of assessment can enable road managers to detect road distresses quicker and address them faster to minimize civilian exposure to road hazards.
Project PAVE is funded by DOST PCIEERD and led by Dr. Lea Bronuela-Ambrocio, faculty member of UP ICE Transportation Engineering Group.
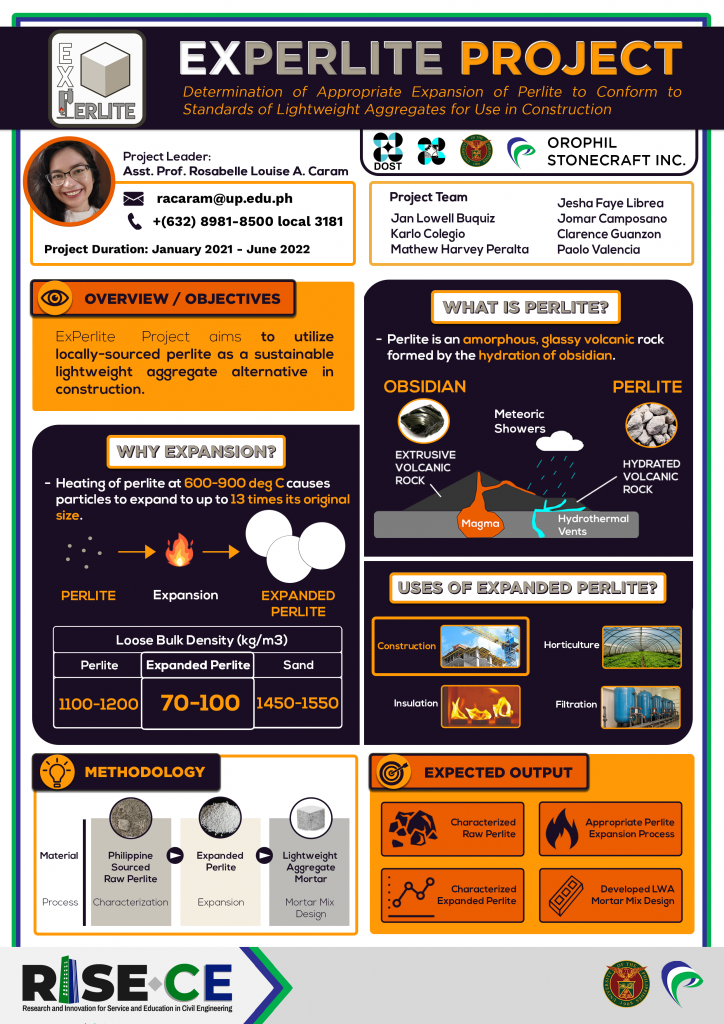
ExPerlite – Determination of Appropriate Expansion of Perlite to Conform to Standards of Lightweight Aggregates for Use in Construction
Project ExPerlite aims to determine a suitable expansion process for Philippine perlite for use in construction. Perlite, once heated, has been found to expand up to 20x in size while maintaining a bulk density about 3x less than mixing sand. The use of expanded perlite (EPA) as a light-weight partial or full replacement to sand in construction can reduce the dead load of the structure, which could then lead to the reduction of the sizes of structural members and ultimately, the overall cost of the structure.
Project ExPerlite is conducted in partnership with Orophil Stonecraft, Inc., and funded by DOST PCIEERD . It is led by Asst. Prof. Rosabelle Louise Caram, faculty member of UP ICE Construction Engineering and Management Group.
